A complete guide to MAC addresses on Mac
Nearly all devices today — computers, smartphones, tablets, routers, speakers – are “smart” or connected to the internet in some way. And all of them need to talk to each other by sending various packets of information. You’ve probably heard one way of doing so is through an IP address. But there’s also another, more permanent device identifier — a MAC address.
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is permanent because it’s assigned to your devices at the lower hardware level, rather than the higher software level for the IP address. You can think of it as a VIN (vehicle identification number) as opposed to an IP address’s license plate. Similarly, you can’t get an IP address if you don’t have a MAC address first.
So what is a MAC address exactly? How is it used? How do you locate it? Can you be traced through it? Can you change it? Let’s explore these and other questions in our comprehensive MAC address guide.
What Is A MAC Address Exactly?
Every network-connected device has a unique MAC address assigned by its manufacturer. But why?
Essentially, what a MAC address does is manage the NIC (network interface controller), or network adapter, that you need to connect to any network, be it Ethernet, WiFi, or Bluetooth. For any devices to communicate, one must send information to another’s MAC address.
A MAC address is a string of six two-character combinations (both numbers and letters). Are MAC addresses case sensitive? No. They can be upper or lowercase (although not mixed), and divided by colons, dashes, or written together.
So a MAC address example could be something like 21-22-EJ-8C-D2-99. The rules by which MAC addresses are created is managed by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers). Sometimes, certain companies choose to assign similar MAC string combinations to their devices, so they can easily find device by MAC address if need be.
How is a MAC address and IP address different?
When you just learn about MAC addresses, it can be difficult to differentiate them from IP addresses, which more people are familiar with. So what’s the difference?
Both MAC and IP are critical to any network, and they work well together. MAC addresses function on a low level between devices on the same network. IP addresses can venture out of the same network by using a router.
But you can’t just rely on IP addresses. To assign an IP address in the first place, your router will use your device’s MAC address. In other words, no MAC — no IP. And without an IP address, your device won’t connect to the outside network at all.
The benefits of using MAC addresses
You might wonder if there are any other benefits to MAC addresses besides enabling IP addresses. The answer is yes!
For example, since MAC addresses are permanently assigned to all network devices, they are also a great way to filter out unwanted devices from your network. So security teams around the world construct corporate firewalls that only allow specific MAC addresses in. In this case, even if a certain IP address changes, the device will still be able to pass through.
More specifically, if a device goes missing or gets stolen, you can identify device by MAC address when it connects back to your network.
Additionally, you can find a geo-location of your Mac using its MAC address.
All these use cases also mean that it’s paramount for you not to reveal your MAC address to anyone to avoid spoofing.
How to find your MAC address
By now, knowing what is a MAC address and what it’s used for, you might want to know where do you actually locate one on your Mac. And there are few ways to do so.
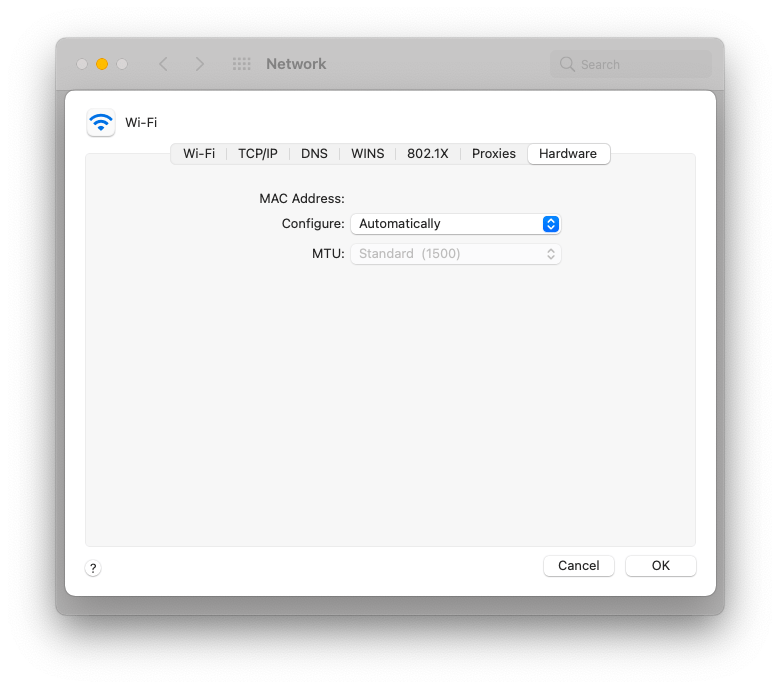
The most straightforward way to look up your MAC address is through System Preferences:
- Open System Preferences ➙ Network
- Click Advanced…
- Switch to the Hardware tab
- Record your MAC address
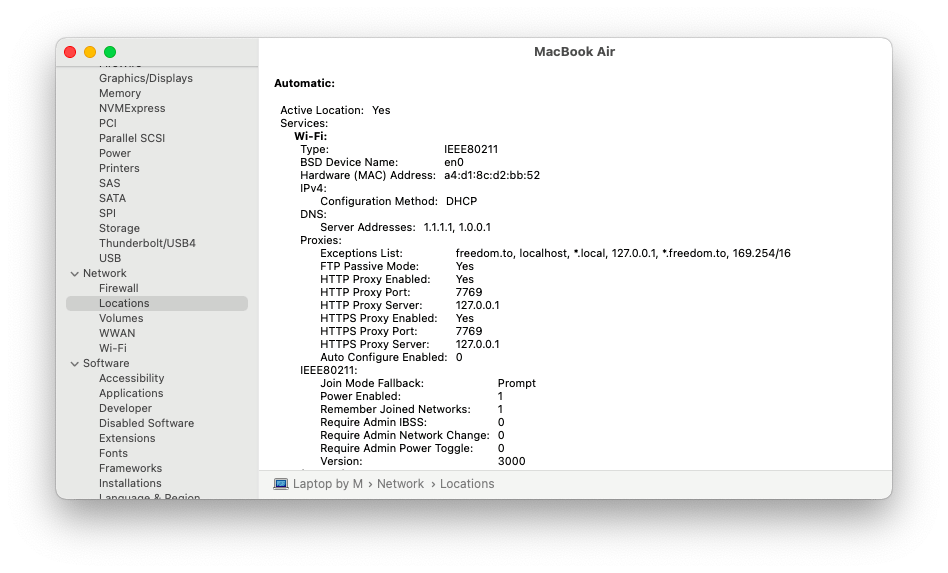
Another way to find your MAC address is through System Report:
- Click the Apple icon in the menu bar ➙ About This Mac
- Go to System Report…
- Switch to Network ➙ Locations
- Record your MAC address
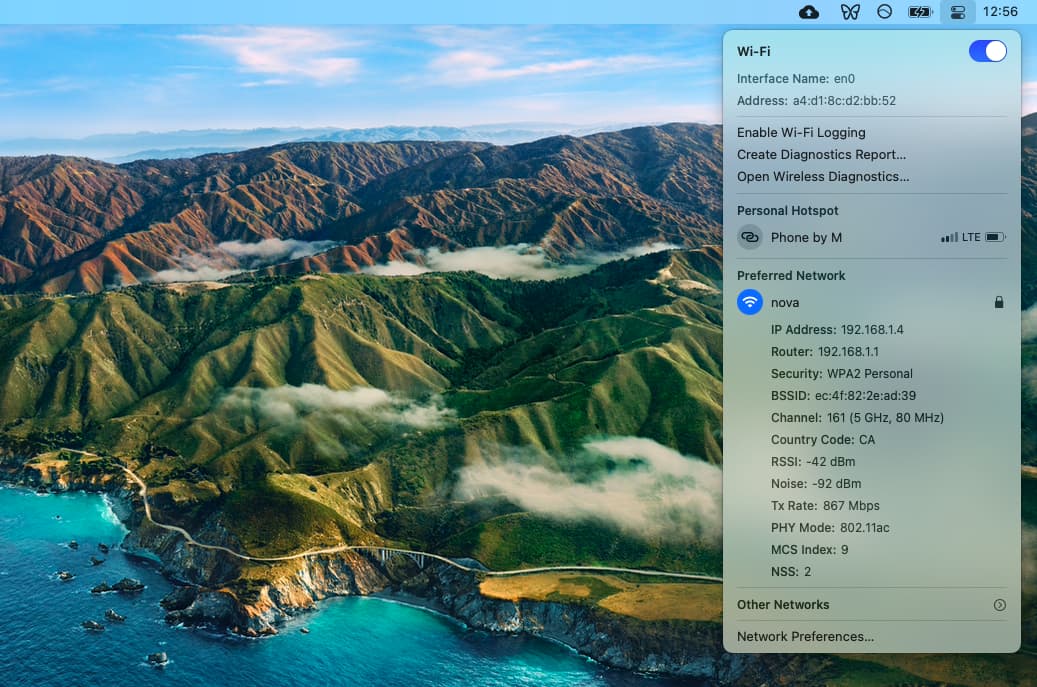
The easiest way to figure out a MAC address is via Wi-Fi options:
- Click Control Center in the menu bar
- Option + open WiFi
- Your MAC address is the same as BSSID
Additionally, it’s also easy to find a MAC address on your iPhone:
- Go to Settings ➙ General
- Tap About
- Your iPhone’s MAC address is the same as Wi-Fi Address or Bluetooth
On most other network devices (e.g. routers), the MAC address is actually written at the bottom.
But what’s an easier and more informative way to look up a router’s MAC address from anywhere?
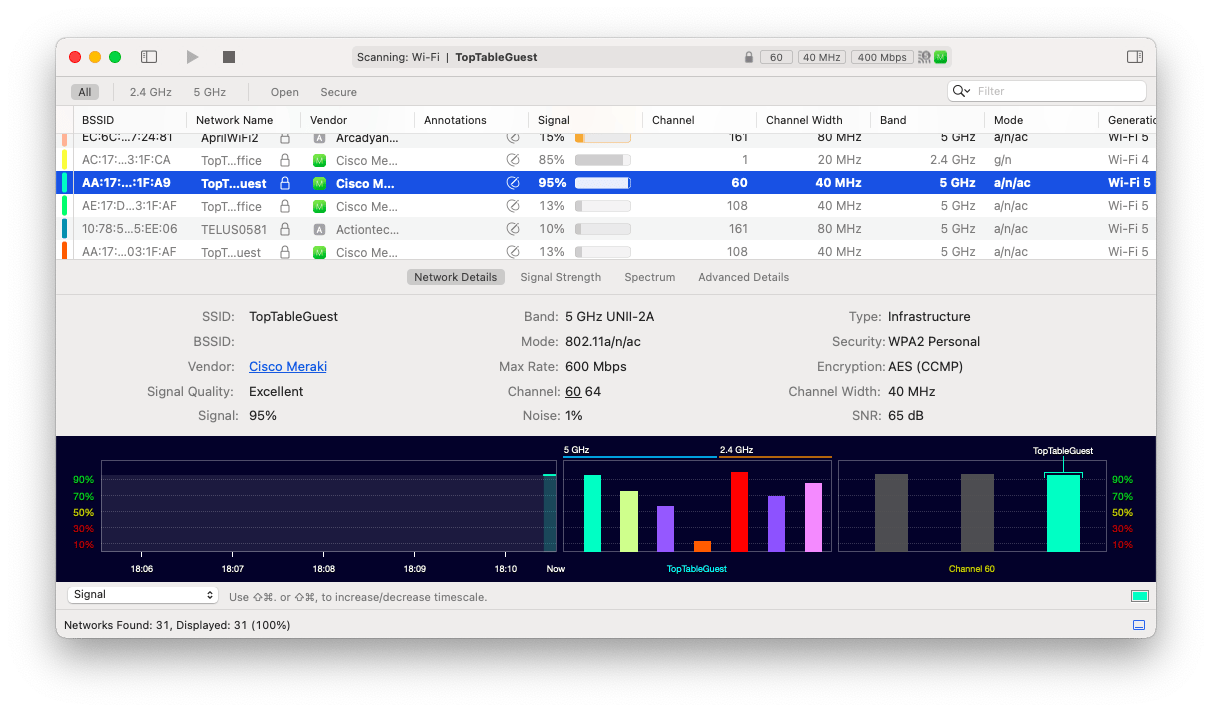
WiFi Explorer is by far the most advanced analytical tool for your network. At a glance, this app gives you all possible information you could need, from your router’s MAC address (BSSID) to noise levels, to signal strength, to channel width, and more.
You also get real-time visual graphs that let you identify any issues and fix them with a built-in troubleshooting guide. A comprehensive network solution!
Alternatively, take a look at NetSpot. While the app is similar to WiFi Explorer in terms of the information it gives you and its troubleshooting capabilities, what sets NetSpot apart is an accurate WiFi signal test across your space. Simply upload a plan of your home or draw one and test how the signal changes in different rooms. Once you have a precise map, you can decide to add WiFi extenders, for example, to make the internet faster everywhere.
How to change MAC address
As mentioned above, MAC addresses are like VINs, which is to say permanent and assigned to a device by its manufacturer. So it’s not possible to actually change your MAC address for good.
At the same time, you can sort of spoof your MAC address at the software level, to give someone a perception that your MAC address is not what it really is. This is what hackers do to get into corporate networks — that’s why revealing your real MAC address can be dangerous. And that’s also why you might want to change it, especially when you’re on a public WiFi.
Here’s how to change MAC address on Mac:
- Disconnect from your WiFi network, but don’t turn off WiFi completely
- Launch Terminal from Applications ➙ Utilities
- Enter sudo ifconfig en0 ether [your desired MAC address]
That’s it. Your new MAC address will last until you restart your Mac, router, or WiFi. So it’s a good temporary solution that’s easy to reverse at any time. Make sure to copy-paste it to your notes if you’re going to use it frequently!
As you can see, a MAC address plays a crucial role in your Mac’s network connectivity. Moreover, there are a few ways for how to find your MAC address and how to find the MAC address of your router using WiFi Explorer and NetSpot. Finally, changing your MAC address can be done with a single Terminal command.
Best of all, WiFi Explorer and NetSpot are both available to you absolutely free for seven days through the trial of Setapp, an extensive platform with more than 200 Mac apps that can help you with pretty much anything, from managing your menu bar (Bartender) to having an infinite clipboard (Paste). Try every Setapp app today at no cost and expand your personal collection of favorites!





