8 must-know Mac Terminal commands (updated for 2026)
▼ Key Takeaways: Terminal commands on Mac
- Terminal unlocks hidden Mac features you can't access through System Settings. Commands like showing hidden files, changing screenshot formats, and customizing the Dock give you control beyond the graphical interface.
- Most Terminal commands are reversible and safe to experiment with. You can undo changes by running the same command with the opposite setting (like changing TRUE to FALSE), making it beginner-friendly.
- Navigation commands are your foundation. Master pwd (print current directory), cd (change directory), and ls (list files) to move confidently through your file system from the command line.
- Visual apps can replace many Terminal tasks if you prefer a graphical interface. Tools like Path Finder, CleanShot X, Lungo, Sidebar, and Trickster offer the power of Terminal commands with user-friendly controls. Try them all with a 7-day free trial on Setapp.
If you’ve never used Terminal commands on your Mac, the interface might look unfamiliar at first. But Terminal is straightforward once you understand the basics. Learning a few essential Mac Terminal commands can help you unlock powerful features and streamline your workflow.
You don’t need to dive deep into UNIX technicalities to get started with these practical commands. This guide covers the most useful Terminal commands for everyday Mac users, along with tips for troubleshooting, productivity, and app recommendations that extend your Mac’s capabilities.
8 best Mac Terminal commands
The best Terminal commands for Mac depend on what you want to achieve. First, let’s make sure you know how to open Terminal on Mac:
- Open Finder.
- Go to Applications > Utilities.
- Double-click Terminal.
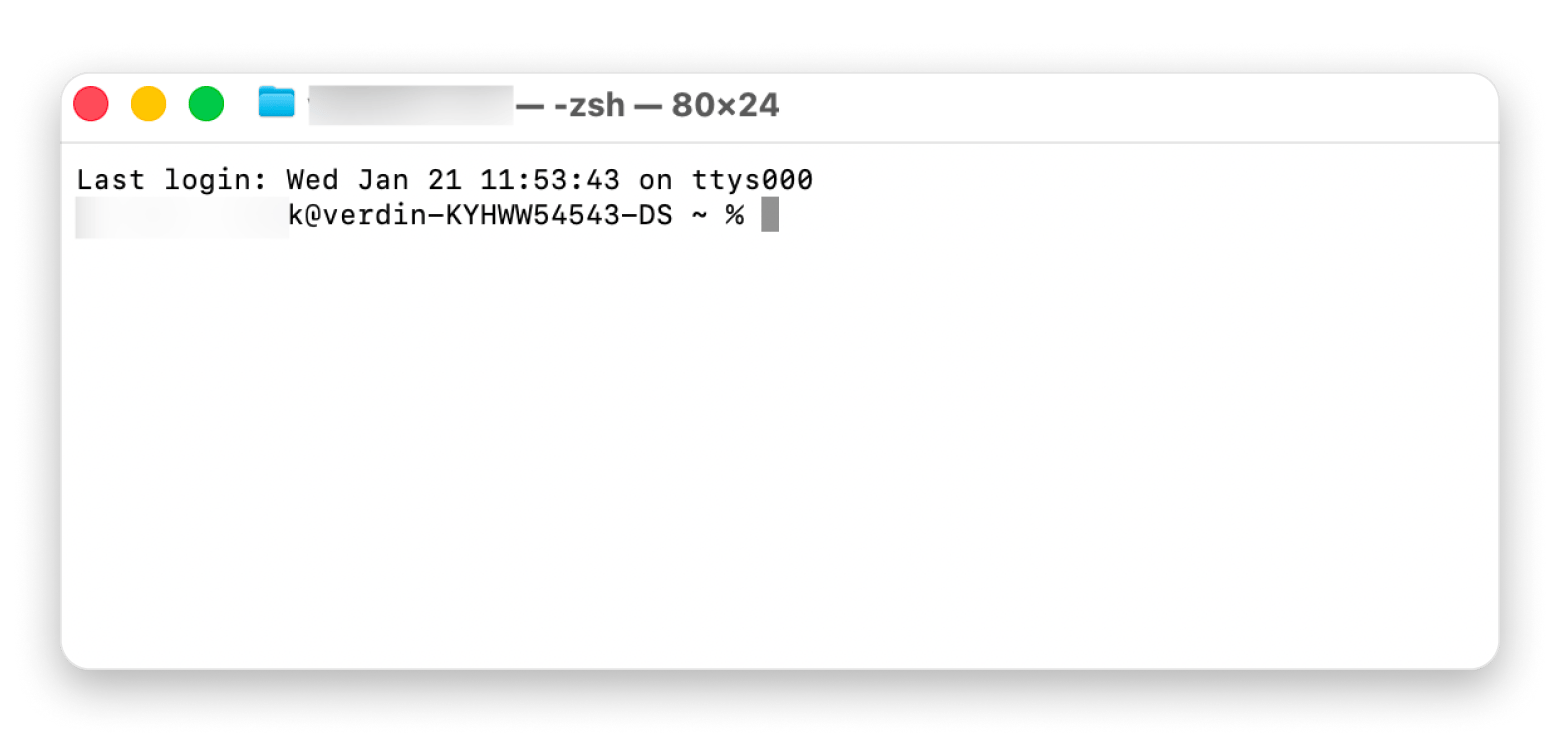
A Terminal window will appear, showing your Mac’s name and your username. You’ll enter all commands after the “%” prompt, pressing Return to execute.
Navigation cheat-sheet for beginners
Here are three essential navigation commands:
- pwd — print the current directory
- cd — change directory (cd .. goes up one level)
- ls — list files (add -l for detailed view)
Let’s walk through some of the most useful commands you can try.
Command 1: Show or hide hidden files and folders
macOS allows you to reveal hidden files and folders in Finder using a Terminal command.
To show hidden files and folders, type:
defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles -bool TRUE
killall Finder
To hide them again, change TRUE to FALSE and run the commands again.
Command 2: Duplicate files between folders
The ditto Terminal command lets you copy files or entire folders from one location to another on macOS.
To do so, type:
ditto [source_folder] [destination_folder]
For a detailed (verbose) output, add the -v flag:
ditto -v [source_folder] [destination_folder]
Read more on the Apple ditto main page.
Command 3: Change default screenshot settings
macOS lets you customize where screenshots are saved and which file format they use by running Terminal commands.
To set a new location, type:
defaults write com.apple.screencapture location ~/your/desired/location
killall SystemUIServer
To change the file format (e.g., to JPEG) type:
defaults write com.apple.screencapture type jpg killall SystemUIServer
Check out the quick-fix guide when screenshot on Mac not working.
Command 4: Remove drop shadows from screenshots
macOS adds a drop shadow by default when you take a screenshot of a window. You can disable this behavior using a Terminal command.
To disable drop shadows on window screenshots:
defaults write com.apple.screencapture disable-shadow -bool TRUE killall SystemUIServer<code></code>
Change TRUE to FALSE to re-enable shadows.
Command 5: Download files without your browser
macOS lets you download files directly from the command line using the curl tool. This is useful for quick, single-file downloads when you already have the file’s URL.
Follow these steps:
Change to your Downloads folder:
cd ~/Downloads/
This ensures the file is saved to your Downloads directory.
2. Download the file:
curl -O https://website.com/path/to/file
3. The -O flag saves the file with its original name.
The -O flag tells curl to save the file using its original filename.
Once the command finishes, the file will appear in your Downloads folder without opening a web browser.
Learn more in the Apple curl man page.
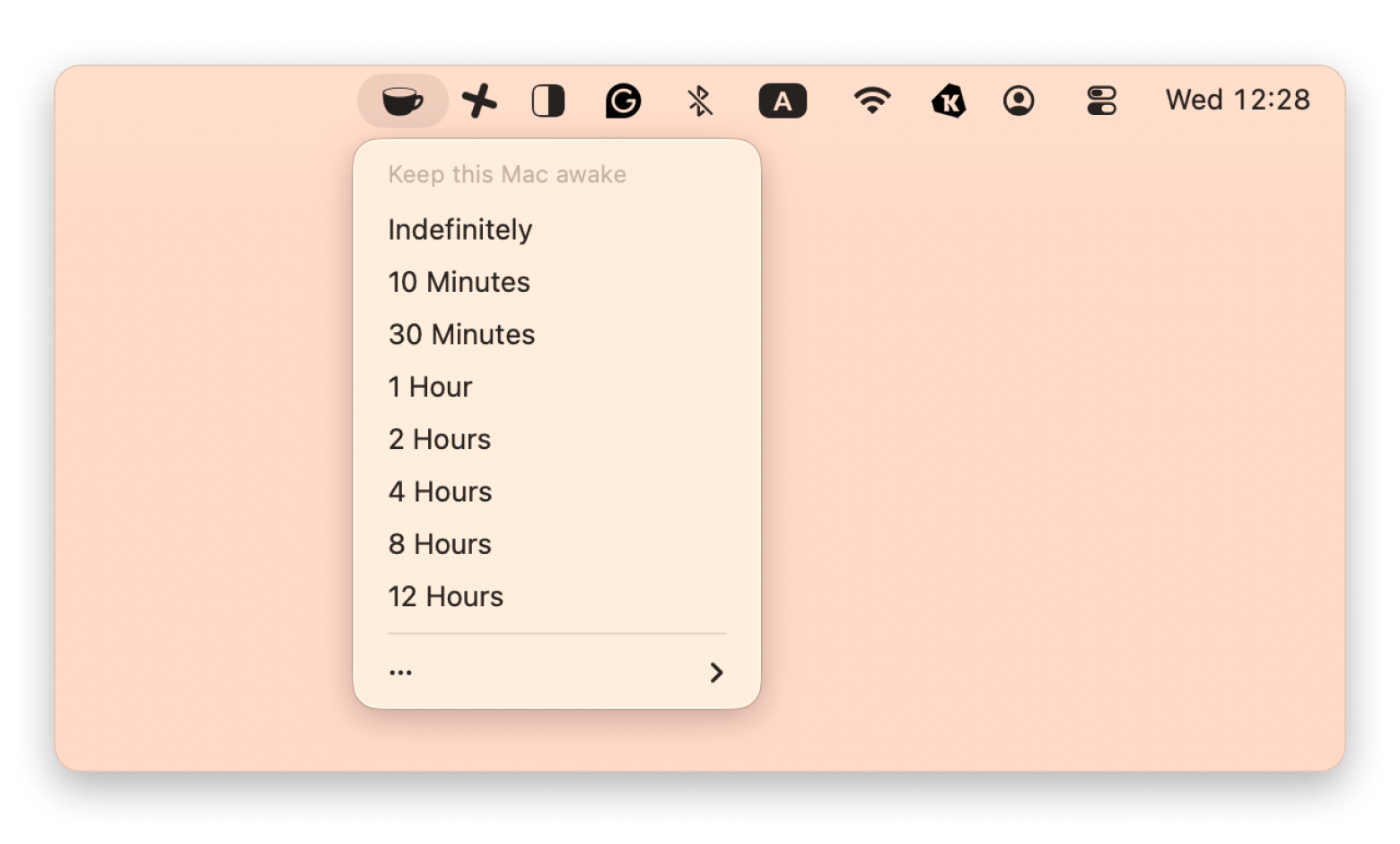
Command 6: Keep your Mac awake temporarily
macOS includes a built-in command called caffeinate, designed to prevent your Mac from going to sleep for a set period of time.
To keep your Mac awake, type:
caffeinate -u -t [number_of_seconds]
Replace [number_of_seconds] with how long you want your Mac to stay awake.
If you prefer a simpler, visual option, apps like Lungo let you keep your Mac awake with a single click from the menu bar:
Command 7: View the contents of any file
To display the contents of a file in Terminal:
cat ~/path/to/file.txt
This is especially handy for recovering text from corrupted documents. Learn more about cat.
Command 8: Hide inactive apps in the Dock and dim hidden ones
To show only active apps in your Dock, type:
defaults write com.apple.dock static-only -bool TRUE killall Dock
This removes inactive apps from the Dock and displays only apps that are currently running.
To dim icons for hidden apps, type:
defaults write com.apple.Dock showhidden -bool TRUE killall Dock
Hidden apps will appear dimmed in the Dock, making it easier to see which apps are active but not visible.
If you want a more flexible Dock replacement, Sidebar offers a customizable app bar designed for improved multitasking and window management.
Read also
Troubleshoot Mac issues without Terminal
While Terminal commands are powerful, you can often solve Mac problems with intuitive apps. They provide user-friendly interfaces for tasks like file management, screenshot capture, and system optimization. Here are the two best tools I use to troubleshoot without Terminal.
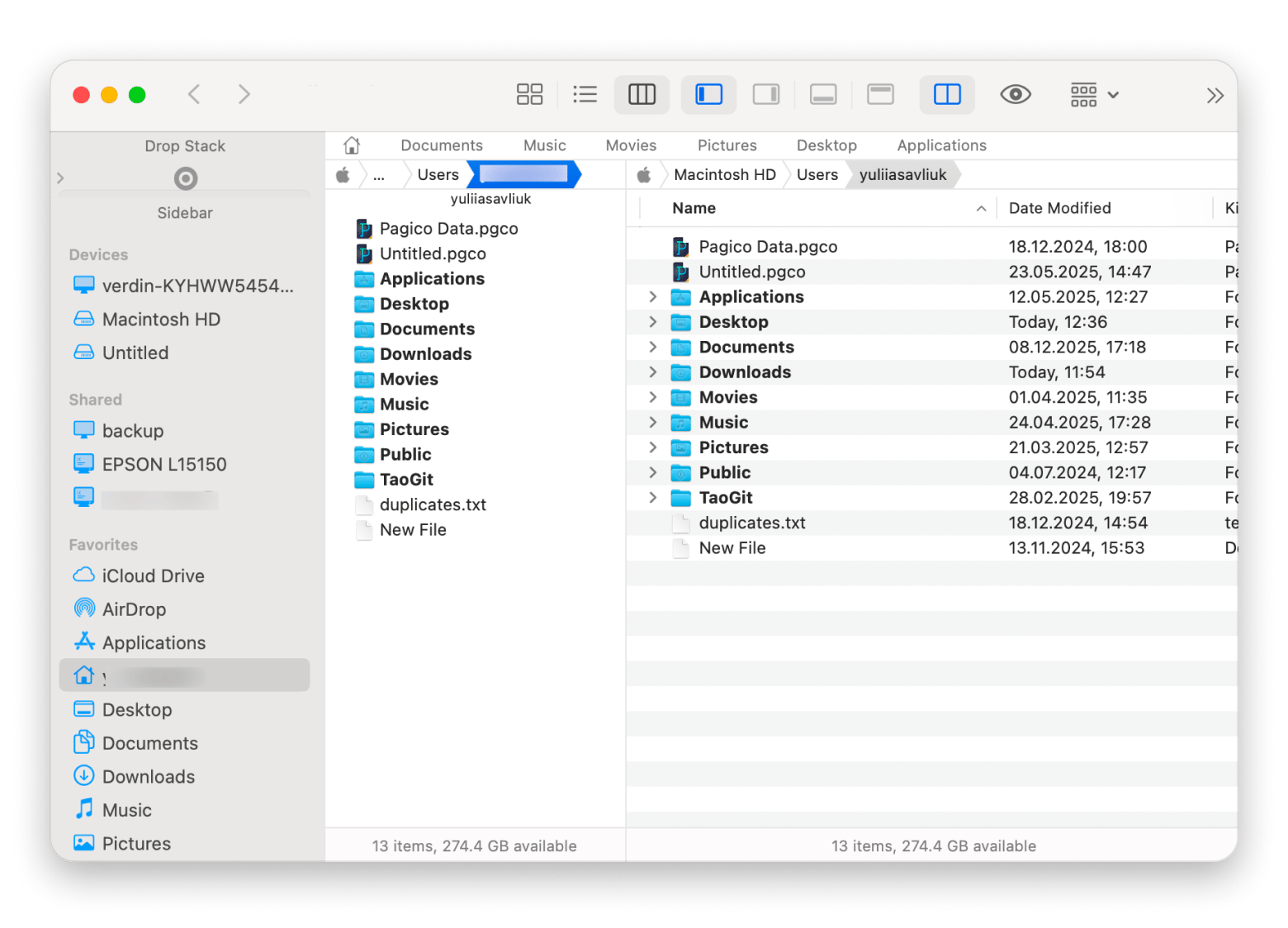
Path Finder: File manager with advanced features
Path Finder is a file management tool that extends Terminal’s capabilities and adds features you won’t find in Finder or Terminal alone:
- Modular interface lets you add or remove features like file info and permissions
- Dual-pane view for faster file operations
- Drop Stack for temporary storage and batch actions
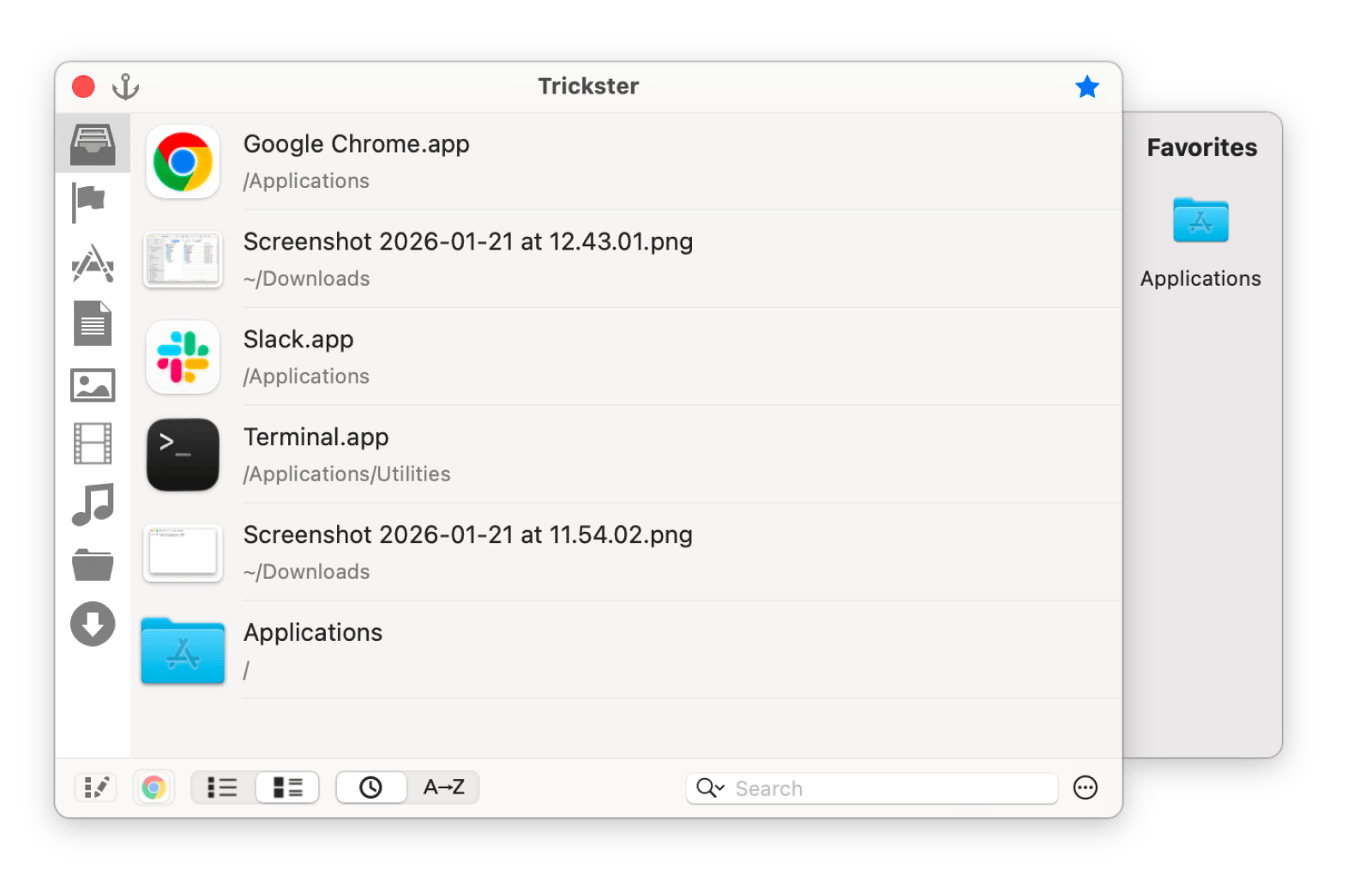
Trickster: Quick access to recent files
Trickster helps you quickly access recent files and actions on your Mac. It also:
- Tracks recently used files and folders for fast retrieval
- Configurable tracking for specific file types or locations
- Streamlines your workflow by keeping important files one click away
Why the Terminal window still matters
Many Mac users haven’t explored Terminal commands, which means they’re missing out on some powerful built-in capabilities. Terminal provides access to features and shortcuts that aren’t available in macOS’s graphical interface.
Most changes made with Terminal can be reversed by running the command with the opposite setting (like changing TRUE to FALSE). This makes it a safe way to explore advanced Mac features.
You can even play simple games in Terminal. Try this:
- Open Terminal and type emacs, then press Return.
- Press Escape, then type x tetris (or pong or snake), and press Return.
For a fun surprise, watch an ASCII version of Star Wars:
telnet towel.blinkenlights.nl
It’s a fun way to see what Terminal can do beyond practical commands.
8 must-know Mac Terminal commands for everyday users
Learning a few Mac Terminal commands can significantly expand what you’re able to do on macOS, without needing deep UNIX knowledge.
For beginners, Terminal works best as a power tool for specific tasks, not a replacement for Finder. Most commands take effect immediately and can be undone by reversing a setting, making them safe to experiment with.
If you prefer visual tools, apps like Path Finder, CleanShot X, Lungo, Sidebar, and Trickster can replicate or extend many Terminal workflows with a graphical interface — often saving time for daily tasks. The coolest part is you can check out all these apps and over 260 security-tested Mac apps on Setapp. It’s a subscription platform with curated apps, and you can try all the premium features with a 7-day free trial.
FAQ
How do I open Terminal on my Mac?
To open Terminal:
- Open Finder.
- Navigate to Applications > Utilities.
- Double-click Terminal.
Tip: You can also pin Terminal to your Dock for quick access.
What are some basic Terminal commands every beginner should know?
Here’s a quick cheat sheet of basic Terminal commands for beginners:
- pwd — show the current directory
- ls — list files in the directory
- cd — change directory
- cd .. — go up one directory
- mkdir [foldername] — create a new folder
- cp [source] [destination] — copy files/folders
- mv [source] [destination] — move or rename files/folders
How do I run a script or program in Terminal?
To run a script or program in Terminal:
- Make the script executable and type: chmod +x script.sh > Press Return.
- Run the script, type ./script.sh > Press Return.
- For Python or other interpreters, type python3 script.py > Press Return.
Is it safe to use the rm command?
The rm command deletes files immediately, bypassing the Trash. Double-check your file path before using it. For extra safety, use rm -i to prompt for confirmation, or manage files with an app like Path Finder, which provides an undo option.